Herniated discs are a common back ailment. The amount of pain and the level of treatment you may require as you heal will depend on what kind of herniated disc you have. There are three types of herniated discs. They are defined by the level of damage to the disc.
When broadly defined, herniated discs are a condition where the soft tissue around the spinal cord gets irritated and inflamed. This causes pain and discomfort in the back and neck. The pain usually starts at the lower back and radiates down the legs.
The three types of herniated discs are:
– Contained herniation
– Disc extrusion or non-contained herniation
– Sequestered herniation
In this article, we will discuss the details of each type of herniated disc and the symptoms that accompany each one, treatment options, and how you can prevent herniated discs.
Background: Anatomy of the Spine
Before discussing the types of herniated discs, it is helpful to provide some background on the anatomy of the spine.
The adult skeletal spine is made up of 26 vertebrae. They are made up of two parts: the body and the arch. The arch is the part that connects the vertebrae together.
Intervertebral discs are located between each vertebra in the spine. They act as shock absorbers for the spinal column and allow movement of the spine. The discs also help protect the spinal nerves from damage.
The disc is comprised of two sections: the annulus which is a rubbery outer layer, and the nucleus which is the jelly-like middle section.
The spine itself is divided into separate sections. These include the cervical spine, the thoracic spine, and the lumbar spine.
– The cervical spine is comprised of seven vertebrae that make up the neck. It is a common site of herniated discs.
– The thoracic spine has twelve vertebrae. Herniated discs are not as common in this space.
– The lumbar spine, the low back region, has five lumbar vertebrae and is the most common location of herniated discs.
Herniated discs can occur at any point along the spine. Symptoms can change depending on the location of the herniated disc along the spine.
What Causes Herniated Discs?
Herniated discs are caused when the disc between two vertebrae becomes damaged. This damage may be due to trauma, such as a car accident, or it may be due to degenerative changes in the spine.
Traumatic injuries cause tears within the disc. Degenerative changes result in wear and tear over time. As these processes continue, the disc loses its ability to function properly. When the disc fails, it bulges outwards causing pressure on surrounding tissues. This results in inflammation and irritation of those tissues.
Contained Herniation
A contained herniated disc is also known as disc protrusion or a bulging disc. This type of herniated disc occurs when the jelly-like nucleus of the disc is damaged and presses on the annulus. The annulus then may press on sensitive spinal nerves.
A contained herniation is usually mild. Indeed, it is possible to have a contained herniation and not even notice.
In other instances, a contained herniation might be slightly more acute. In these cases, symptoms tend to range from mild to moderate. The more pressure on the nerves that surround the spinal cord the more pronounced the symptoms.
Symptoms include pain, discomfort, and slight tingling in the arms or legs.
With all types of herniated discs, tingling and burning, sensations in the arms and legs will depend on the location of the injury. For example, tingling in sensations in one or both of the arms is most often caused by cervical spine herniation. Tingling and burning in the legs are caused by disc herniation in the lumbar spine.
Conservative treatment options for contained herniation include rest, applying heat, and over-the-counter anti-inflammatories like acetaminophen. Rarely do contained herniations require more aggressive treatment.
Disc Extrusion or Non-Contained Herniation
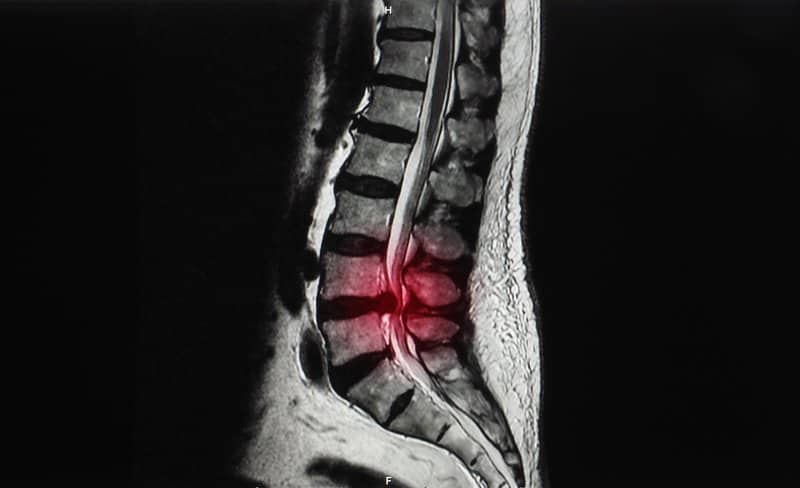
Disc extrusion or non-contained herniation occurs when the nuclear of the disc ruptures and spills into the annulus. This causes pressure on nearby nerve roots and, in some cases, the spinal cord itself.
Painful symptoms are inevitable with disc extrusion. Tingling and burning sensations are more common with this type of herniated disc. These symptoms will range from moderate to severe.
A physical examination from a medical professional may be necessary to develop a treatment plan for this type of injury.
Treatment options include rest, applying heat, pain medications, physical therapy, steroid injections, and more innovative options like radiofrequency ablation.
Uncomplicated disc extrusion should heal on its own without the need for surgery. Although, disc extrusions that do not respond to conservative treatments may qualify for non-invasive surgical options.
Sequestered Herniation
Of the three types of herniated discs, sequestered herniation is often the most severe. It occurs when the nucleus erupts out of the outer layer of the disc. The ruptured disc material can migrate to different locations along the spinal canal and become trapped.
Sequestered herniation can happen as a result of untreated disc extrusion.
This condition commonly results in severe pain, loss of mobility, and spinal stenosis.
Treatment choices for sequestered herniation include all of the conservative options and noninvasive surgery. Recovery time will depend on the extent of the disc sequestration.
As this is a more serious type of disc herniation, treatment should be discussed with a medical professional. They will provide a physical examination as well as any medical imaging like an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) that will help determine the extent of your injury.
Treatment for Herniated Discs
Treatment depends on how severe the pain is, whether there is an underlying cause, and how long the patient experiences pain. Most cases resolve themselves without treatment, however, many people experience recurring episodes that need further evaluation.
As noted above, there are many treatment options for herniated discs. The level of treatment intervention will depend on the type of herniated disc and how well the individual responds to treatment. Treatment can be separated into three categories: conservative treatments, noninvasive surgical options, and surgery.
Conservative treatments
Rest
The first step in treating a herniated disc is to stop doing anything strenuous until you have seen a doctor. If you feel fine after resting then it’s okay to go back to work but make sure you tell your employer about your injury so they know what to expect if you start feeling worse again.
Heat Therapy
Applying hot packs to sore areas helps reduce inflammation and relax muscles. You can use heating pads, ice bags, or even warm water bottles. Heat therapy has been shown to improve recovery times by up to 50%.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers such as Acetaminophen, Ibuprofen, Naproxen Sodium, Aspirin, etc., can also help relieve muscle spasms and stiffness associated with herniated discs.
Physical Therapies
Exercise programs designed specifically for people who suffer from lower back injuries can help strengthen weak abdominal muscles and increase flexibility. Stretching exercises can also help prevent future problems.
Steroid Injections
These types of injections contain cortisone which reduces swelling and relieves pain. Steroids can take several weeks before their full effects kick in.
Non-Invasive Surgery Options

If conservative measures fail to alleviate symptoms, some patients choose to undergo minimally invasive procedures. These surgeries involve injecting steroids into the affected area through small incisions rather than making large cuts open surgically. This allows doctors to inject directly at the site of the problem while minimizing damage to surrounding tissue.
Radio Frequency Ablation
A newer option involves using high-frequency waves to destroy nerve endings near the source of pain. It works best when used along with other treatments because it requires multiple sessions over a period of months.
Lumbar Fusion
A lumbar fusion is performed when two vertebrae become fused together due to degenerative changes. This procedure may be recommended if conservative methods do not adequately treat chronic low back pain. Lumbar fusions require extensive rehabilitation following surgery.
Spinal Decompression
This technique uses special tools to remove pressure off nerves and blood vessels within the spinal canal. Spinal decompressions are typically done under local anesthesia and only last around 30 minutes.
Surgery
When all else fails, surgical repair may be necessary. A surgeon removes damaged tissues and replaces them with healthy ones. Surgeries usually include removing bone fragments, repairing ligaments, and inserting artificial materials between bones. Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the condition.
Preventing Disc Herniation
With some thoughtful preventative measures, you can limit your chances of getting any of the three types of herniated discs.
Proper posture
Practicing proper posture while sitting, standing, and walking can help protect your spine from disc herniation.
Avoid lifting heavy objects
Lifting heavy objects puts undue stress on your back muscles which increases your risk of developing a herniated disc later in life.
Maintain healthy weight
Carrying excess weight is a risk factor for herniated discs. This is because it adds extra stress on the spine. In particular, weight carried in the abdomen can strain the spine of the lumbar region.
Regular exercise
One of the best ways to prevent disc herniations is to exercise regularly. If you do not exercise, then you should start doing some light exercises such as walking for 30 minutes per day. Also, implementing strengthening exercises will build strength in the muscles that support the spine.
Herniated Discs Treatment at MidSouth Pain

If you are experiencing persistent back pain, contact the pain management specialists at MidSouth Pain.
MidSouth Pain offers comprehensive care for patients suffering from chronic lower back pain or sciatica caused by a herniated disc in Memphis TN. Our team includes board-certified physicians who specialize in treating these conditions using minimally invasive techniques. We also offer state-of-the-art diagnostic testing including advanced magnetic resonance imaging.
For those seeking relief from their painful symptoms, schedule a consultation today!